What is That Sound?
Tinnitus: symptoms, causes, and coping mechanisms
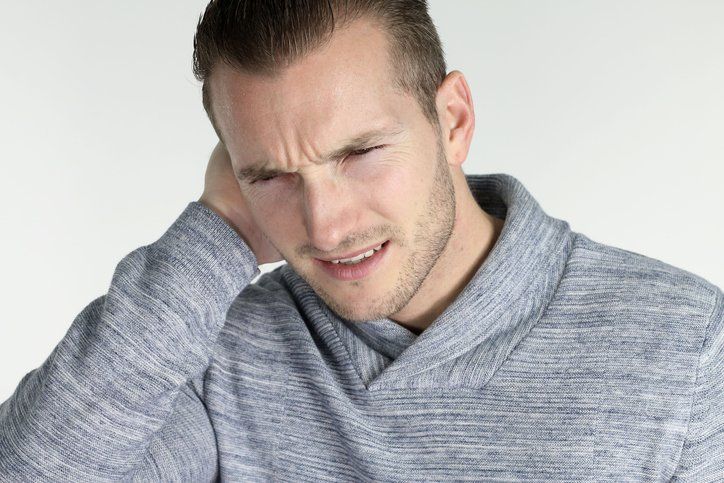

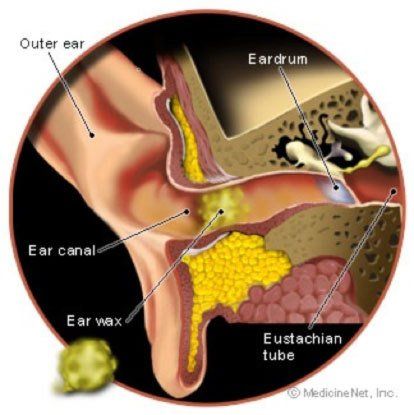
| Hearing ringing, buzzing, clicking, or hissing sounds when no external sound is present are signs of tinnitus. These sounds can come and go, or be bothersome all the time. This health condition is commonly caused by age-related hearing loss, exposure to loud noises, earwax blockage, or abnormal bone growth. Some less common causes include Meniere’s disease, TMJ disorder, head injury, neck injury, and acoustic neuroma. Tinnitus can negatively impact your quality of life, so it’s best to see a hearing specialist. In the meantime, there are coping strategies you can try:
Excessive noise, nicotine, caffeine, alcohol, and aspirin can aggravate tinnitus. If you work in a loud environment, wear ear protection to minimize your exposure to loud sounds.
A white-noise machine with soothing sounds of a waterfall, ocean waves, birds, etc. can help you relax and fall asleep. Even turning on a fan at night can help.
Since hearing aids amplify other sounds, they can draw attention away from the tinnitus. Talk to us about how hearing instruments can be helpful.
Stress can intensify tinnitus symptoms, so take some time to devote yourself to stress management techniques. Whether it’s getting a massage, going to a yoga class, or taking a walk, stimulating endorphins can help.
The best way to address any hearing problem is to sit down with hearing specialists, like us, for a hearing screening. At Bieri Hearing Specialists in Saginaw, MI, audiology is our area of expertise. Together, we can discuss your tinnitus symptoms, possible causes, and coping mechanisms to try and relieve you of any discomfort. |